As the global emphasis on sustainability intensifies, engineers are increasingly turning to Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) to create environmentally friendly products. By leveraging simulation tools, CAE facilitates the design of greener solutions that minimize waste, reduce energy consumption, and promote sustainable practices throughout the product lifecycle. Caliber Technologies has supported projects in this area, leveraging our expertise in engineering simulations. Here’s how CAE is revolutionizing sustainable design.
1) Material Optimization
One of the key benefits of CAE is its ability to analyze and optimize materials. Engineers can simulate different materials and their properties, helping them select the most sustainable options for their designs. This process can reduce material waste and ensure that only the necessary amount of material is used, minimizing the environmental impact.
2) Lifecycle Assessment
CAE tools enable engineers to conduct comprehensive lifecycle assessments (LCA) of products. By simulating every stage of a product’s life—from raw material extraction to production, use, and end-of-life—engineers can identify potential environmental impacts and areas for improvement. This holistic view helps in making informed decisions that promote sustainability.
3) Energy Efficiency Analysis
Simulation tools allow engineers to evaluate energy consumption in product designs. By analyzing how products interact with energy sources and environments, CAE can help optimize designs for energy efficiency. For example, in building design, CAE can simulate natural light usage and HVAC performance, leading to more energy-efficient structures.
4) Waste Reduction
By conducting simulations to identify design flaws early in the process, CAE significantly reduces waste. Engineers can test multiple iterations without the need for physical prototypes, ensuring that only the most effective designs move forward. This approach not only saves materials but also decreases the overall carbon footprint of the product development process.
5) Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
CAE can simulate and optimize manufacturing processes, allowing engineers to identify more sustainable methods of production. By analyzing factors like energy use, emissions, and waste during manufacturing, companies can adopt practices that reduce their environmental impact while maintaining product quality.
6) Design for Disassembly
Sustainability also involves considering the end-of-life of products. CAE enables engineers to design products with disassembly in mind, facilitating easier recycling and repurposing of materials. By simulating how a product can be taken apart, engineers can ensure that components can be reused or recycled effectively, reducing landfill waste.
7) Innovation in Sustainable Technologies
The integration of CAE with emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, allows for the exploration of innovative sustainable solutions. Engineers can simulate complex systems and analyze vast datasets to uncover new approaches to sustainability, driving innovation in product design.
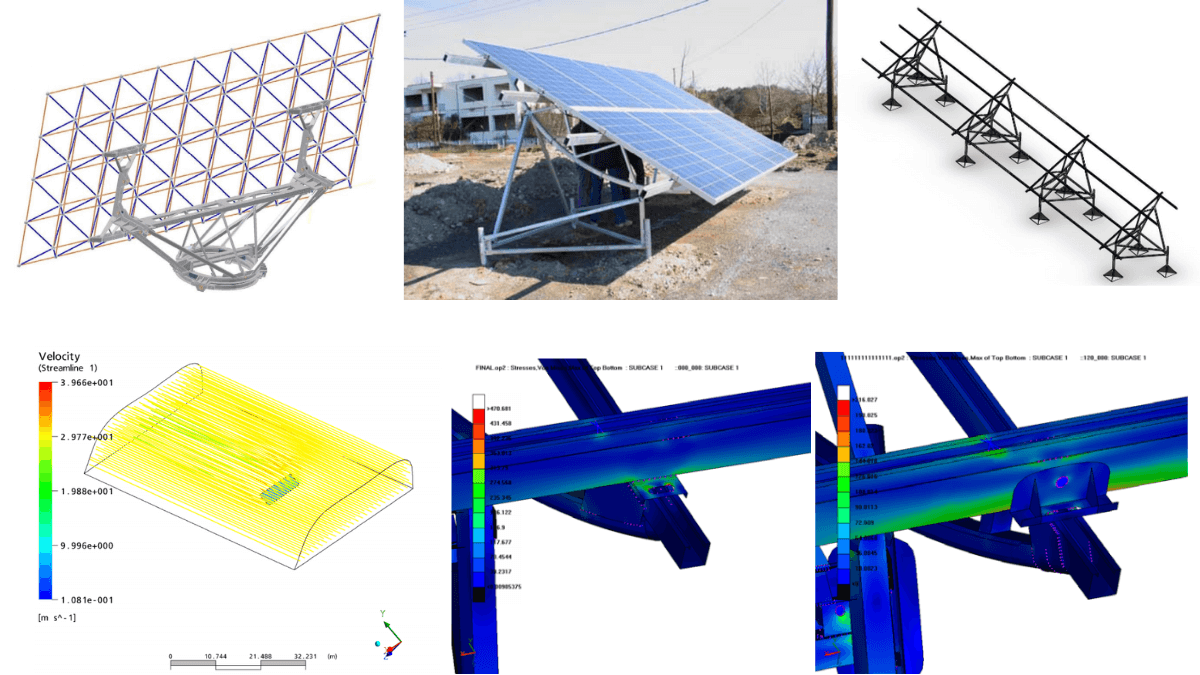
Figure: Solar structure analysis for wind load, strength, durability, and thermal performance
Conclusion
The marriage of sustainability and CAE is paving the way for greener products that meet the demands of both consumers and the environment. By utilizing simulation tools, engineers can make informed decisions that minimize waste, optimize resources, and enhance energy efficiency throughout the product lifecycle. As industries continue to face pressure to adopt sustainable practices, the role of CAE in facilitating eco-friendly designs will only grow in importance.
In a world where environmental considerations are paramount, embracing CAE not only positions companies as leaders in sustainability but also contributes to a healthier planet for future generations. By designing greener products through simulation, engineers are making a significant impact on sustainability, ensuring that innovation aligns with ecological responsibility.